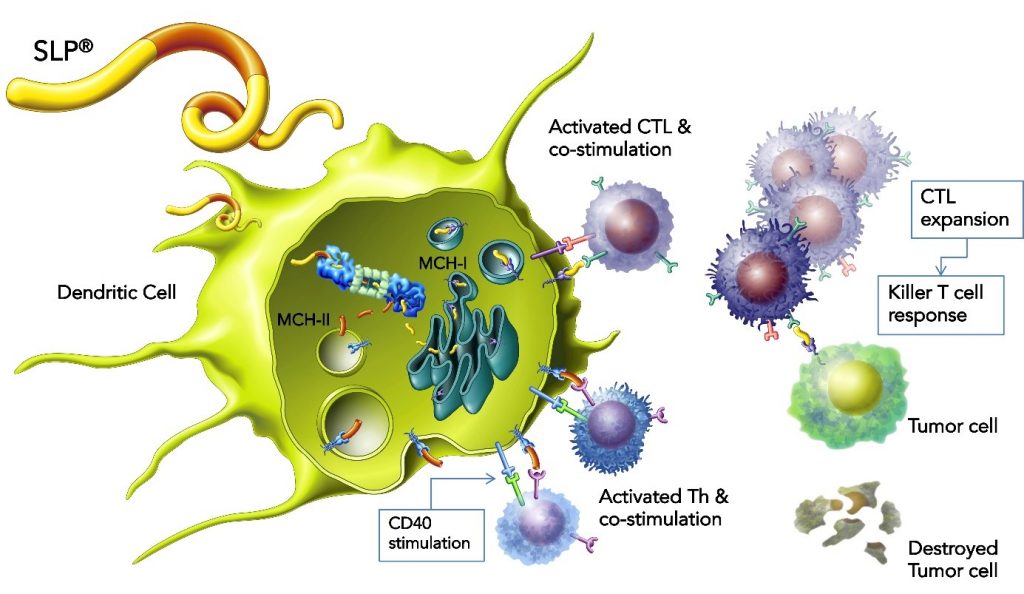
Synthetic Long Peptide processing & mechanism of action
- The long peptide is taken up by the dendritic cell.
- The long peptide enters the dendritic cell, where it is degraded into small pieces, containing epitopes recognized by T cells. The epitopes are a mix of T helper (Th) epitopes and cytotoxic T cell (CTL) epitopes. The T helper (Th) epitopes enter the MHC Class II presentation pathway via the endosomes. At the same time, the Cytoxic T Lymphocyte (CTL) epitopes enter the MHC class I presentation pathway, after proteasomal digestion.
- T cell receptor binding to MHC-epitope complex, co-stimulation and T helper signals ensure optimal activation of the CTL (or CD8 killer T cell). This activation leads to expansion of the CTL.
- Active CTLs will move to tumor cells that express the same epitopes via the MHC class I presentation.
- The T cell receptor on the CTL recognizes MHC-peptide complexes on tumor cells and these activated T cells specifically kill the tumor cells, leaving normal cells intact.
- In addition, active Th cells can also destroy tumor cells directly, or indirectly through activation of tumor-associated macrophages.
We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. Ok